If you need further tests including a brain scan, ECG or scan of blood vessels the doctor will ask you to take a seat back in the waiting room. The nurse will then show you where to go for these tests which can normally performed on the same day.
Heart tests
Sometimes strokes are due to clots in the heart passing up the blood vessels to the brain.
- The doctor may therefore organise an electrocardiogram to check the heart rhythm.
- echocardiogram to look at the heart structure.
- 24 hour tape to monitor the heart rhythm.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The electrocardiogram measures the electrical activity of your heart.
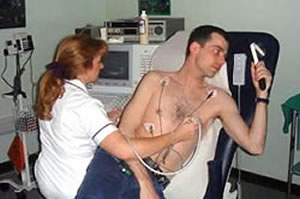
Echocardiogram
The Echocardiogram scan uses sound waves to take pictures of the heart.
Holter – 24 hour ECG tape
This involves having stick on electrodes on the chest connected by wires to a small box which is attached to a belt around the waist. This is left on for a day and night. The person goes home with the monitor on and carries on with normal activities.
Blood vessel tests
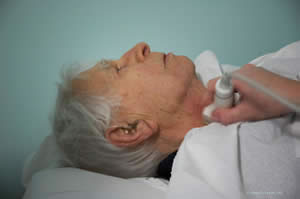
Duplex scan of blood vessels
Sometimes strokes are caused by narrow blood vessels in the neck. Clots can attach on to these narrow areas to block the vessel or the clots can fly off into the brain to cause a stroke. The Duplex scan uses sound waves to take pictures of the blood vessels in the neck and to measure the blood flow through them. It is performed in the X Ray department on the floor above the clinic.
Brain scans
Strokes are due to part of the brain being damaged. This occurs when a blood vessel blocks or bursts.
A brain scan can identify whether a blood vessel has blocked or burst. If the stroke is mild then sometimes the brain scan is normal but usually it will show the damaged area.
CT scans
CT brain scan uses X-rays to take pictures of your brain and can show up areas of damage. The inside of the machine rotates which allows
x-rays of the head to be taken from different angles. These are used later by computers to make an image of a cross-section of the brain.
MRI scan
The MRI scanner uses magnetism to take very detailed pictures of the brain. It does not use any form of x-rays and although stronger than the earths magnetic field, it is considered completely safe. The MRI scanner is a large tube that is open at both ends. The scanner is fitted with lights and a fan. There is a mirror to allow you to see the radiographer during some types of scan. The machine can be rather noisy and some people find it claustrophobic.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
If the doctor suspects an irregular brain wave rhythm which might occur in an epileptic seizure he may organise an electoencephalogram (EEG). It involves sticking electrodes on the scalp connected by wires to a machine.














