In order for your body to recover from surgery, it needs the right energy and nutrients. A healthy balanced diet is important to help prepare your body for surgery.
Being overweight or underweight can both increase the risks when having an operation. It is therefore important to try to achieve a normal body weight before your operation or treatment.
Aim for a healthy weight, a normal Body Mass Index (BMI) is between 20-25 kg/m². Watch out for eating problems and if you have trouble eating (like swallowing or dental issues) seek help.
You should aim to eat three regular meals with a good balance of the food groups – protein, carbohydrates and healthy fats. Try to avoid adding any extra sugar or salt to your diet.
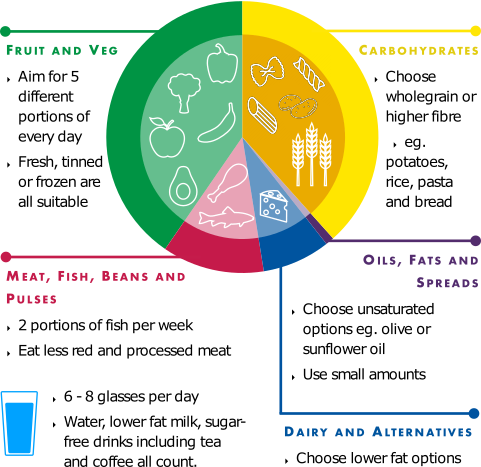
Balanced Diet
Fruit and Veg
Aim for 5 different portions of fruit and veg every day.
Fresh, tinned or frozen are all suitable.
Carbohydrates
Choose wholegrain or high fibre for example potatoes, rice, pasta and bread.
Oils, Fats and Spreads
Choose unsaturated options for example olive oil or sunflower oil and use small amounts.
Dairy and Alternatives
Choose lower fat options.
Meat, Fish, Beans and Pulses
2 portions of fish per week
Eat less red and processed meat
Liquids
6-8 glasses per day.
Water, lower fat milk, sugar free drinks including tea and coffee all count.
Benefits of improving nutrition prior to surgery
- Improves your wound healing
- Lowers your risk of infection
- Could result in a shorter hospital stay
- Feeling more energetic
- Better weight management
Energy needs
Carbohydrates are the body’s main fuel source which are represented in yellow on the eat well plate. Under eating these foods can lead to a lack of energy, low mood, and reduced concentration.
Overeating carbohydrates especially when physical activity is low can cause weight gain.
Prior to your surgery we recommend meeting the advised portion sizes for carbohydrates and spreading them throughout your meals.
Wholegrain options are recommended due to the nutrients they contain and the fibre content which is good for bowel health.
Protein needs
Protein is the body’s main fuel for building muscle and strength.
You may need to build some strength prior to your surgery. Ensuring your protein intake is adequate can help with this.
Protein also plays a vital role in your immune system. Some excellent sources of protein are chicken, meat, fish, eggs, greek yoghurt, nuts and lentils.
Meat is a source of protein, Iron and B12 however it is known that excessive intakes can be linked to colorectal cancer. It is therefore recommended to keep to a limited daily intake ( 70g) and avoid processed, high fat and high salt options.
Hydration
Drinking enough water is essential for energy levels, brain function, digestion and helps to regulates temperature.
Drinking enough fluids can help make you feel your best.
The minimum daily fluid recommendations are 1600mls for women and 2000mls for men, unless there is a clinical condition that requires a different approach.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals.
We can get adequate amounts from diet.
Having a well-balanced diet rich in micronutrients can help with immune function, wound healing, muscle function and antioxidant protection.
In the UK during autumn and winter everyone is advised to take a supplement containing 10 micrograms (400 international units) of vitamin D per day to support general health and in particular bone and muscle health.
This is because we cannot make vitamin D from sunlight at this time of year.
Poor appetite and/or weight loss
Depending on why you’re having surgery, some people may actually lose weight without trying before their operation.
It is important your body has good energy stores to recover after surgery.
If you have lost weight without trying to, or have a reduced appetite, try these simple changes to stop any more weight loss:
- Eat little and often – try 5-6 small snacks or meals per day.
- Take drinks after meals and not before.
- Use full fat milk and full fat dairy products.
- Add margarine or butter to mashed potatoes.
- Add grated cheese and/or cream to soups and sauces.
Where to Get Help
For Non Cancer Nutrition advice
NHS Eat Well
Check out their website for tips on healthy eating.
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well
British Dietetic Association
Information on eating well and nutrition.
https://www.bda.uk.com/resource/healthy-eating.html
Cancer Nutrition and Prehabilitation
For further information on Cancer Nutrition and Prehabilitation please visit the Scottish government prehab website.
https://www.prehab.nhs.scot/prehab-and-me/diet-and-nutrition
Macmillan Cancer Support
The Building-up Diet Booklet has suggestions on how to help boost energy and protein intake when appetite is poor. It explains healthy eating and how foods are used in our bodies. There are sample menus, and a suggested shopping list of items that may help when preparing meals.
The Stay Healthy – eat a healthy diet easy read booklet uses a mixture of simple language and images
Other lifestyle support resources are available on the Macmillan website















