BPPV is a common type of dizziness where people suffer short episodes of vertigo triggered by particular head movements.
The vertigo typically lasts for 2-20 seconds. Common triggers include turning over in bed, getting out of bed or tilting the head to look up. Sometimes the vertigo is accompanied by a feeling of nausea.
What is BPPV?
BPPV is a common type of dizziness where people suffer short episodes of vertigo triggered by particular head movements. The vertigo typically lasts for 2-20 seconds. Common triggers include turning over in bed, getting out of bed or tilting the head to look up. Sometimes the vertigo is accompanied by a feeling of nausea.
Benign: this means that it is due to a non serious cause
Paroxysmal: this refers to the fact that the dizziness comes in short bursts
Positional: this refers to the fact that the dizziness is triggered by certain positions, for example turning over in bed
Vertigo: is dizziness where it feels like the world is spinning around you
What causes BPPV?
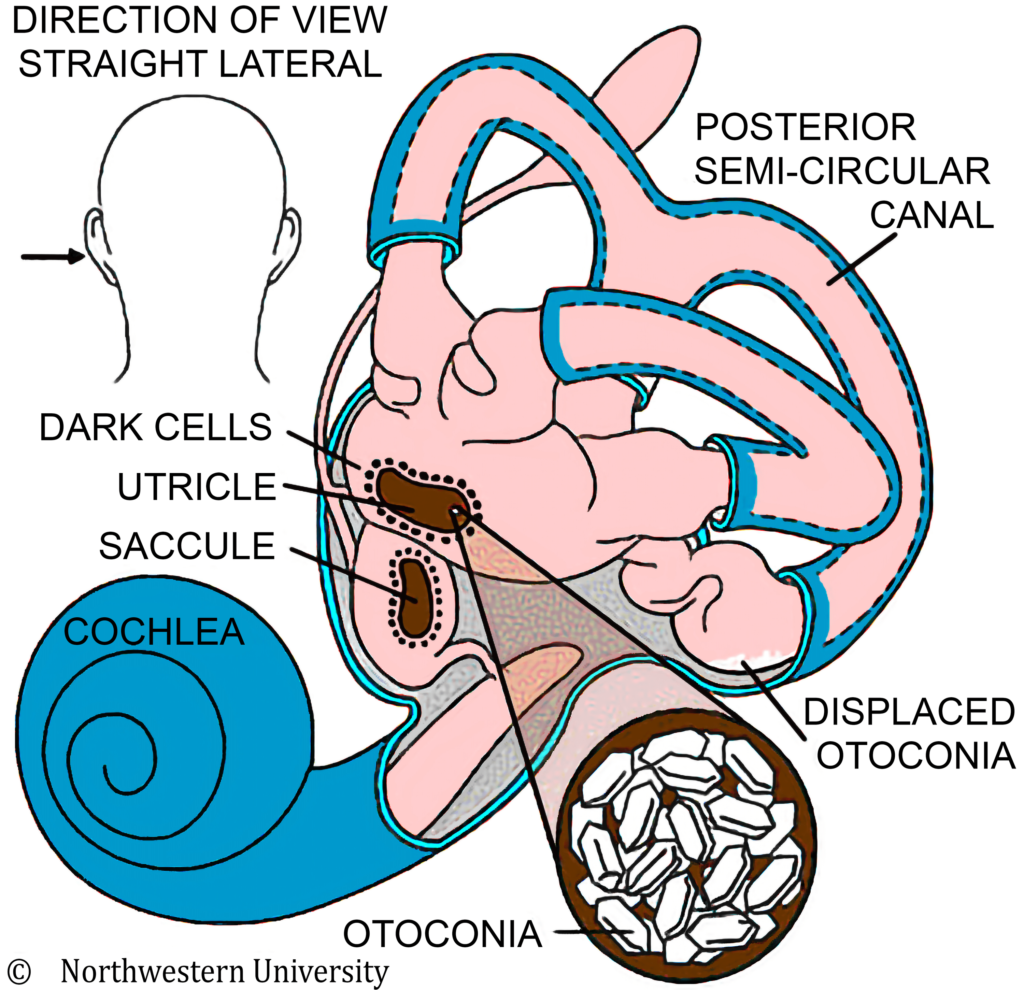
The balance part of the inner ear is made up of three fluid filled semicircular canals and the utricle and saccule. Within the utricle and saccule are crystals of calcium carbonate known as “otoconia”. Sometimes these crystals become loose and find their way into one of the semicircular canals. Certain head movements then cause the crystals to move within the canal. This then causes extra movement of the fluid in the canal which is what causes you to feel dizzy.
https://dizziness-and-balance.com/images/bppv/bppv-otoconia-cd.gif
Testing for BPPV
The most common test for BPPV is the Dix-Hallpike test, which might be carried out in our clinic or by your GP. In this test you sit on the couch with your head turned to one side. We then ask you to lie back as quickly as possible. You then stay in that position for thirty seconds while we look for movements of your eyes that indicate BPPV. If you have BPPV you are likely to feel dizzy during this test, but the dizziness will be of short duration and should settle quickly.
What is the treatment for BPPV?
The standard treatment for BPPV is to try and move the crystals out of the semicircular canal to where they can no longer cause any dizziness. This is done by leading you through a series of different head positions, normally staying in each position for about thirty seconds. This is called the Epley manoeuvre. The sequence of positions we use depends on which semicircular canal we think the crystals are in. After the final position the crystals should have fallen out of the semicircular canal.
After treatment
After treatment you may feel a little dizzy or unsteady for a few hours. We advise that for 48 hours after the treatment you avoid the movements that caused your BPPV. We also suggest that for this period you sleep with two pillows. This is to reduce the risk of the crystals falling back into the semicircular canals. After the 48 hours we suggest you try the movements that used to make you dizzy. About 80% of the time the BPPV symptoms stop after just one treatment but sometimes we may have to repeat it. In this case we will arrange for further treatments and in some cases home exercises
What should I do if my symptoms recur?
It is not unusual for BPPV to come back after a few months or years. If it does come back you should contact your GP for possible repeat treatment.













